
The most frequent serious adverse reactions reported in ≥2% of patients were pneumonia, pyrexia, diarrhea, pneumonitis, pleural effusion, dyspnea, acute kidney injury, infusion-related reaction, musculoskeletal pain, and pulmonary embolism.
#Checkmate 577 plus#
In Checkmate 743, serious adverse reactions occurred in 54% of patients receiving OPDIVO plus YERVOY. In Checkmate 057, fatal adverse reactions occurred these included events of infection (7 patients, including one case of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia), pulmonary embolism (4 patients), and limbic encephalitis (1 patient). The most frequent serious adverse reactions reported in ≥2% of patients receiving OPDIVO were pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, dyspnea, pyrexia, pleural effusion, pneumonitis, and respiratory failure. In Checkmate 017 and 057, serious adverse reactions occurred in 46% of patients receiving OPDIVO (n=418). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 7 (2%) patients, and included hepatic toxicity, acute renal failure, sepsis, pneumonitis, diarrhea with hypokalemia, and massive hemoptysis in the setting of thrombocytopenia. The most frequent (>2%) serious adverse reactions were pneumonia, diarrhea, febrile neutropenia, anemia, acute kidney injury, musculoskeletal pain, dyspnea, pneumonitis, and respiratory failure. In Checkmate 9LA, serious adverse reactions occurred in 57% of patients (n=358). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 1.7% of patients these included events of pneumonitis (4 patients), myocarditis, acute kidney injury, shock, hyperglycemia, multi-system organ failure, and renal failure. The most frequent (≥2%) serious adverse reactions were pneumonia, diarrhea/colitis, pneumonitis, hepatitis, pulmonary embolism, adrenal insufficiency, and hypophysitis. In Checkmate 227, serious adverse reactions occurred in 58% of patients (n=576). No fatal adverse reactions occurred in patients who received OPDIVO in combination with platinum-doublet chemotherapy. Importantly, we saw long-term benefit among patients with high unmet needs, such as those with PD-L1 expression 2% included pneumonia and vomiting. "The three-year data from CheckMate -9LA demonstrate the ongoing durability with early disease control following treatment with the combination of nivolumab plus ipilimumab, with a short course of chemotherapy. Paz-Ares, M.D., Ph.D., CheckMate -9LA study investigator and chair of the medical oncology department, Hospital Universitario 12 De Octubre in Madrid, Spain. "While immunotherapy treatments have greatly improved outcomes for people with metastatic NSCLC, many patients, particularly those with low PD-L1 expression, are unfortunately not achieving durable, long-term survival," said Luis G. The long-term, durable clinical benefit of Opdivo plus Yervoy with two cycles of chemotherapy was observed at three years across patient populations that typically have a poor prognosis, including patients with PD-L1 expression <1% and squamous histology. With a minimum follow-up of three years (36.1 months), the dual immunotherapy-based combination continued to show sustained improvement in overall survival (OS), the trial’s primary endpoint, with 27% of patients treated with Opdivo plus Yervoy with two cycles of chemotherapy alive compared to 19% of patients treated with chemotherapy alone at three years (Hazard Ratio 0.74 95% Confidence Interval : 0.62 to 0.87).
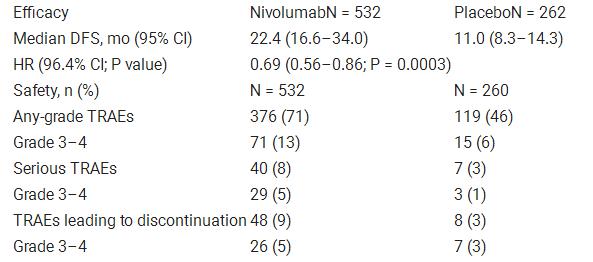
#Checkmate 577 trial#
PRINCETON, N.J., June 06, 2022-( BUSINESS WIRE)- Bristol Myers Squibb (NYSE: BMY) today announced three-year follow-up results from the Phase 3 CheckMate -9LA trial demonstrating durable survival benefits with Opdivo (nivolumab) plus Yervoy (ipilimumab) with two cycles of chemotherapy compared to four cycles of chemotherapy in previously untreated patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (mNSCLC). Late-breaking data to be presented during the 2022 American Society of Clinical Oncology Annual Meeting Dual immunotherapy-based combination resulted in clinical benefits across key subgroups of mNSCLC patients with high unmet need, including those with PD-L1 expression <1%



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
